Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary
Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in northwestern Madhya Pradesh, with one of its boundaries running along the border of Rajasthan. The sanctuary was notified in 1974 and is spread over an area of 368sq.km. Its vast expanse lies within the Mandsaur and Neemuch districts of Madhya Pradesh. River Chambal flows through the sanctuary, dividing it into two parts.
A major part of the sanctuary consists of vast open landscapes with sparse vegetation and rocky terrain, with small patches of dense forests here and there. The principal tree species found in the Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary are Khair, Salai, Kardhai, Dhawda, Tendu, Palash, and the like.
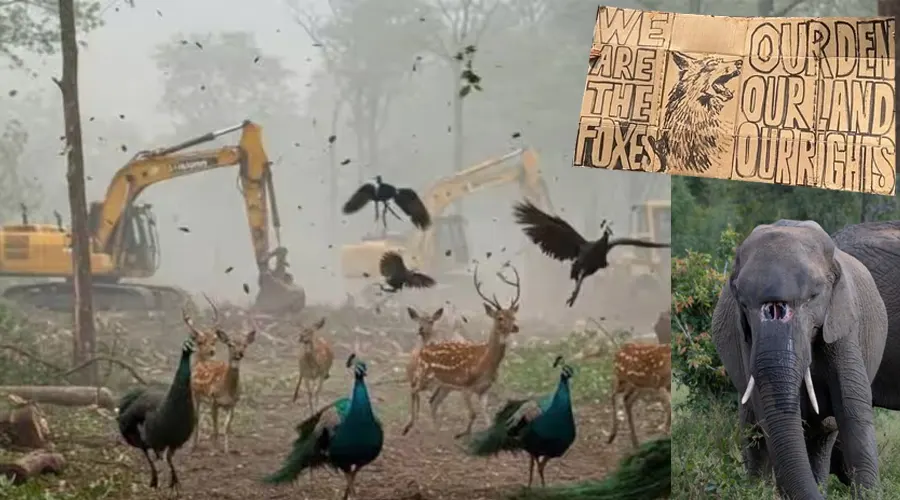
Herbivores like Chinkara, Nilgai, and Spotted Deer, and carnivores like the Indian Leopard, Striped Hyena, and Jackal are found in good numbers in the region. The reservoir also has a good population of crocodiles, fish, otters, and turtles. Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary and the reservoir is also designated Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) as it boasts a large bird diversity with healthy populations.
The sanctuary has attracted more attention after being chosen as a favorable site for the reintroduction of cheetahs in India. Gandhi Sagar has vast open spaces and grasslands interspersed with scrubs, which is the ideal landscape for the cheetah. There is a continuous process of translocating the Spotted Deer from other forest areas to augment the prey base here.